Report from EconoTimes - https://www.econotimes.com/
By Dr. Eunice Anyango Owino*
Dated Monday, 30 October 2023, 10:56 AM UTC - here is a copy in full:
Chad's first dengue fever outbreak: what you should know
Chad has reported its first dengue outbreak, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The country’s health ministry declared an outbreak on 15 August and so far 1,342 suspected cases have been reported, 41 of them confirmed in the laboratory. One death was reported among the patients with lab-confirmed cases. The outbreak started in Ouaddaï province in eastern Chad, currently the outbreak epicentre. Illnesses have also been reported in three other provinces. Godfred Akoto Boafo spoke to medical entomologist Eunice Anyango Owino about the disease.
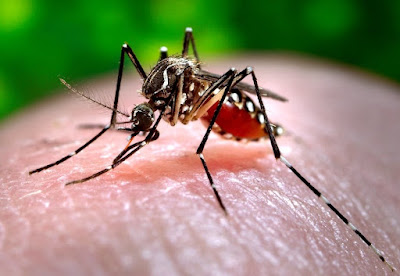
Mosquitoes are the primary medium for contracting dengue. Oregon State University/Flickr
What causes dengue fever and how does it affect people?
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne viral disease caused by one of the four dengue virus serotypes. It is primarily transmitted by the Aedes aegypti mosquito and to a lesser extent the Aedes albopictus mosquito, mainly in the tropical and sub-tropical areas of the world.
Infection with one serotype provides long-term immunity to that particular serotype, but not the others. That means that, after recovery, a person can still be infected by the other three serotypes. Serotypes are groups within a single species of microorganisms, such as bacteria or viruses, which share distinctive surface structures.
Most infections produce only mild flu-like illness; 80% of cases are asymptomatic. But getting infected with different serotypes one after the other puts a person at a greater risk of severe dengue, also known as dengue hemorrhagic fever. It is characterised by serious internal bleeding and organ damage, and a sudden drop in blood pressure that causes shock which can be fatal.
How widespread is it in the Sahel? Why is this first outbreak in Chad significant?
Dengue fever has been endemic in Sudan, with outbreaks documented in 2010, 2013, 2017 and 2019. Unfortunately, due to years of political and civil conflicts, the control and response capacity of the public health sector in Sudan has been limited.
The risk of spread in the Sahel region, which includes Niger, Mali and Chad, has always been high. This is because these countries all host the suitable mosquito vectors (Aedes). They also share the same tropical climate with seasonal heavy rains and floods.
To add to the problem, countries like Chad are grappling with a massive influx of refugees and returnees from Sudan who might be carrying the disease. The epicentre of the current outbreak, the province of Ouaddai at the eastern border with Sudan, hosts more than 400,000 refugees.
The cities at the border with Sudan are densely populated and have poor sanitation. This provides a favourable environment for the vectors to breed.
In addition, Chad lacks effective disease control programmes. This is its first dengue outbreak. It doesn’t have the necessary public health preparedness and response capacities. So the risk posed by this outbreak is high.
The movement of the returning refugees has the potential to spread the outbreak in Chad and even across the border to other countries in the Sahel, the rest of Africa, and the world at large.
What treatment is available?
There’s currently no available treatment for dengue in the world. Timely detection and case management, especially treatment of dehydration and plasma leakage by oral or intravenous rehydration, are key in preventing severe illness and death.
There is an approved dengue vaccine (Dengvaxia) for use in people aged 9-45 years. But for it to be effective they must have had one infection of dengue by any of the four serotype viruses, which must be confirmed by a laboratory test.
The vaccine is given in three doses within 12 months and protects against all the four dengue virus serotypes with an efficacy of 80%. However, its availability in developing countries in Africa isn’t assured, although it has been licensed by several national regulatory authorities.
Apart from the vaccine, the only other guard against dengue fever is prevention of mosquito bites and vector control.
What is the way forward in controlling the disease?
More investment should be put on expanding clinical and laboratory capabilities to deal with the disease.
Given that this is Chad’s first outbreak, it needs to:
• put in place standard operating procedures for clinical management of suspected and confirmed dengue cases
• expand the capacity for early detection of cases – this could be done by procurement of rapid diagnostic tests and by alerting communities
• strengthen disease surveillance and coordinate the response by actively finding cases. Cases within the community are likely to be underreported as dengue is unknown to the public. Also, clinicians might not be familiar with the disease presentation. It could be confused with other common fevers.
• put in place effective vector control measures, like draining stagnant water around residential areas, cleaning and replenishing water storage containers on a weekly basis, distributing insecticide-treated nets, spraying indoors and using window and door screens.
• strengthen surveillance to assess the vector breeding potential in containers and to monitor insecticide resistance. This is critical for selecting the most effective insecticides.
• make communities aware of the risks of infection and how to protect themselves. Engaged communities can take ownership of the vector control strategy and adopt healthy behaviours.
• strengthen cross-border collaboration. The current outbreak most likely spread from Sudan. The focus should be on prevention and vector control measures in border areas.
• mobilise resources for a national contingency plan for dengue preparedness and response. And seek help from experienced organisations like the WHO.
View original: https://www.econotimes.com/Chads-first-dengue-fever-outbreak-what-you-should-know-1665123
*About Author: Eunice Anyango Owino
Dr. Eunice Anyango Owino is a Medical Entomologist based at the School of Biological Sciences, the University of Nairobi, specialising on arthropod borne diseases.
Medical Entomologist at the School of Biological Sciences, University of Nairobi
Source: https://www.econotimes.com/contributors/17080
[Ends]